

- #PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS HOW TO#
- #PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS INSTALL#
- #PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS UPDATE#
- #PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS PASSWORD#
Thus, we have clarified what types of permissions exist and defined what to put in the first part of the GRANT command.
#PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS UPDATE#
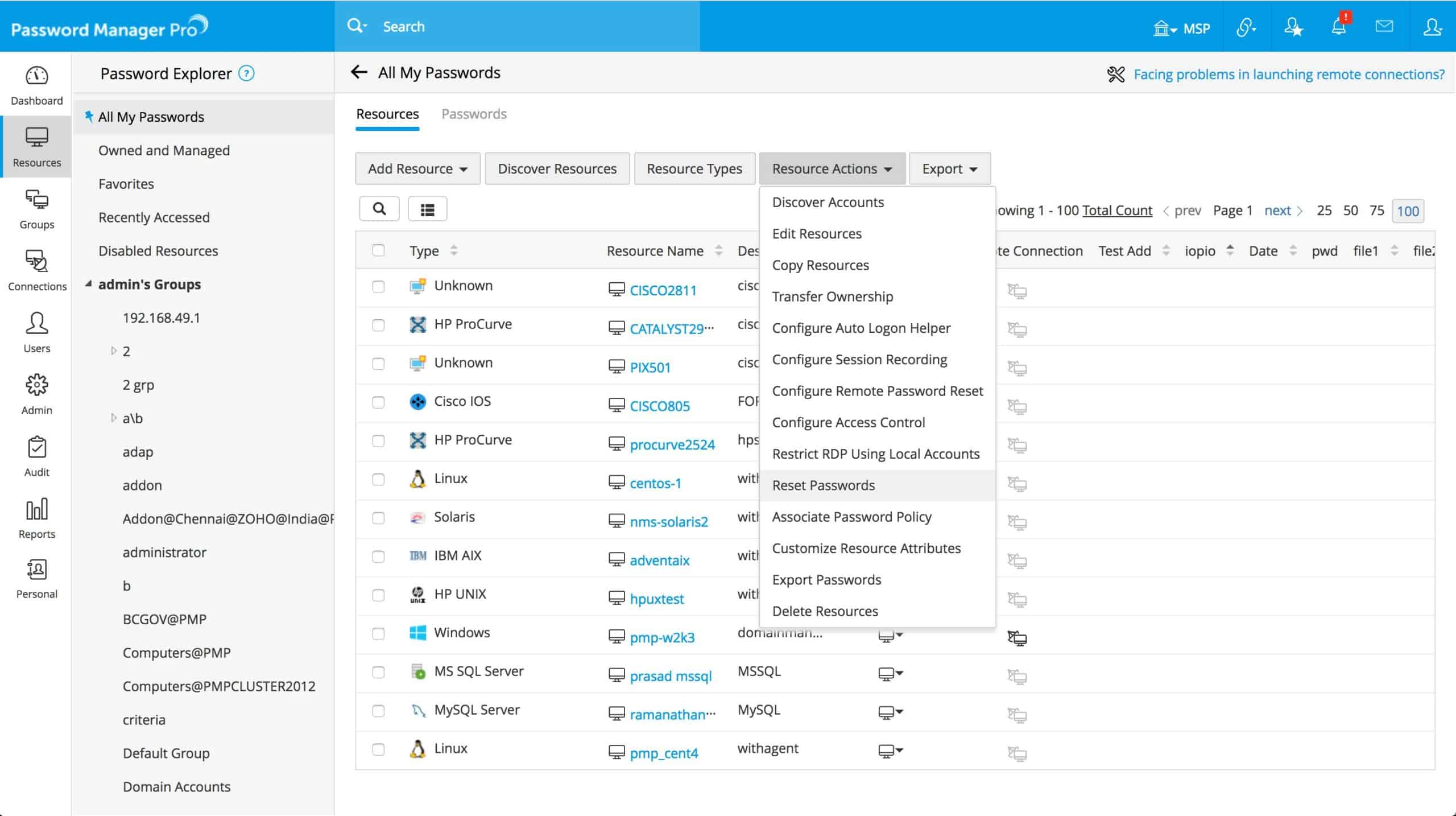
UPDATE – The user gains permission to update table rows.SELECT – The user gains permission to read a database.INSERT – The user gains permission to insert rows into a specific table.DELETE – The user gains permission to delete rows from a specific table.DROP – The user gains permission to drop databases and tables.CREATE – The user gains permission to create databases and tables.ALL PRIVILEGES – The user gains all privileges at an access-specified level.Hence, let’s illustrate the most common types of permissible privileges that can be used for the GRANT and REVOKE statement: TO the above-mentioned syntax is rather basic and doesn’t show all subtleties, it points to the conclusion that there are multiple types of privileges (or permissions) that can be provided to a new user. To provide a user with access to the database and give permissions, you generally need to use the following GRANT statement: GRANT permission_type
#PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS HOW TO#
How to Grant Privileges and Add Permissions to User Otherwise, the user will not have any permissions to reach or manipulate the database in any way. Once you are done with the new user creation, remember to grant privileges to the user to let them access the MySQL database. Note that the IF NOT EXISTS option allows to ensure that the same user has not been created before.
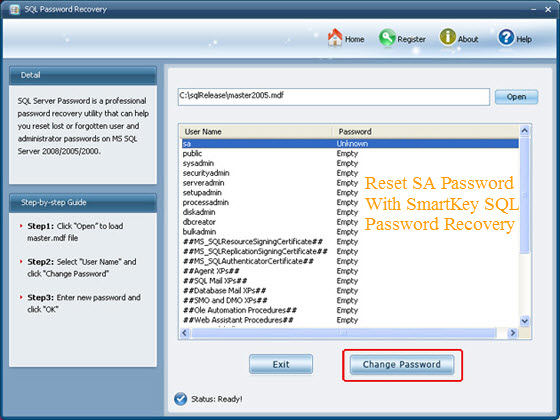
#PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS PASSWORD#
If you want the user to be able to connect from any host, use the ‘%’ wildcard as host_name.įinally, set a password for the new user after the IDENTIFIED BY keywords. If that’s not the case, you can use the remote machine IP address as hostname, for instance: CREATE USER BY 'user_password' Optionally, set the host_name to ‘localhost’ if you want the user to be able to connect to MySQL Server only from the localhost, which means “this computer”. In the syntax above, replace new_user_name with the name of the new user and host_name with the name of the host from which the user connects to the MySQL Server. Let’s have a look at its basic syntax: CREATE USER BY 'user_password' To create a new MySQL user account via the MySQL shell, you need to execute the CREATE USER statement. When you do, you also need to type the password for the root account and press Enter: Enter password: ******** To get started, you need to connect to your MySQL Server instance and log in as a root user via MySQL command-line interface: mysql -u root -p Grant and revoke privileges via Security Manager How to Create a New MySQL User Account via MySQL Shell Create a user account via Security ManagerĨ. Manage users and privileges via dbForge Studio for MySQLħ. Grant privileges and add permissions to userģ. Create a new MySQL user account via MySQL ShellĢ. On top of that, you will have an opportunity to view examples within MySQL shell (MySQL command-line client) as well as within dbForge Studio for MySQL, a GUI tool for MySQL and MariaDB database development, management, and administration.ġ. Moreover, you will have extra practice on how to revoke privileges and remove users from MySQL. You will also find out more about the creation of custom privileges and learn what types of privileges exist in MySQL.
This article provides insight into how to create a new user and grant appropriate privileges on a MySQL database. To put it simply, you will decide on who can do what and with what object types. By doing so, you can give permissions or introduce restrictions within the databases or certain database objects. However, once you decide to let more people access and modify your MySQL database, you need to create users and grant them privileges.
#PASSWORD MANAGER PRO REQURED SQL PERMISIONS INSTALL#
When you install MySQL Server on your system and create a MySQL database, you run the required commands in the MySQL shell as root or administrative user, meaning that you have the full power to control every aspect of your database. Introductionįirst, let’s figure out why we need users and privileges. Learn the basics of user account management and find hints. This article provides a complete overview of how to create a new user account in MySQL and grant different types of privileges on a MySQL database.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
